Reinforced Waterproofing HDPE Geomembrane
Manufacturing Process
Engineering-Oriented Production Steps
HDPE resin formulation and reinforcement material preparation
Precision extrusion of molten HDPE layers
Inline lamination with reinforcement scrim
Calendering for thickness uniformity
Controlled cooling and stress stabilization
Automated inspection for defects and delamination
Roll cutting, labeling, and protective packaging
Key Equipment and Process Controls
Multi-layer extrusion and lamination lines
High-precision calendering rollers
Online tensile and thickness monitoring systems
Quality laboratories for mechanical and hydraulic testing
Product Definition
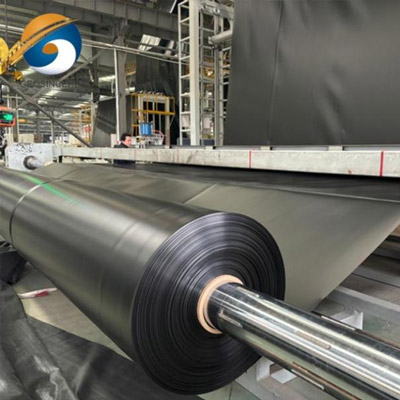
Reinforced Waterproofing HDPE Geomembrane is a composite impermeable lining material engineered by integrating high-density polyethylene with internal reinforcement layers. It is designed to deliver enhanced tensile strength, dimensional stability, and long-term waterproofing performance for critical containment and civil engineering projects.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
The performance of Reinforced Waterproofing HDPE Geomembrane is defined by both polymer properties and reinforcement efficiency. Typical engineering-grade specifications include:
Base Material: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Reinforcement Type: Polyester or woven geotextile scrim
Nominal Thickness: 1.0 mm – 3.0 mm
Sheet Width: 4.0 – 7.0 m
Tensile Strength (MD/TD): ≥ 20 / 20 kN/m
Elongation at Break: ≥ 400%
Hydrostatic Pressure Resistance: ≥ 0.6 MPa
Puncture Resistance: ≥ 450 N
Carbon Black Content: 2.0% – 3.0%
Design Service Life: ≥ 50 years (buried conditions)
Structure and Material Composition
Reinforced Waterproofing HDPE Geomembrane adopts a multi-layer engineered structure to balance flexibility, strength, and impermeability:
Upper HDPE Layer: Primary waterproofing and chemical barrier
Reinforcement Core: Woven or non-woven fabric providing tensile stability
Lower HDPE Layer: Enhances puncture resistance and bonding strength
Stabilizer Additives: Improve UV, oxidation, and thermal aging resistance
Manufacturing Process
Engineering-Oriented Production Steps
HDPE resin formulation and reinforcement material preparation
Precision extrusion of molten HDPE layers
Inline lamination with reinforcement scrim
Calendering for thickness uniformity
Controlled cooling and stress stabilization
Automated inspection for defects and delamination
Roll cutting, labeling, and protective packaging
Key Equipment and Process Controls
Multi-layer extrusion and lamination lines
High-precision calendering rollers
Online tensile and thickness monitoring systems
Quality laboratories for mechanical and hydraulic testing
Industry Comparison
| Material Type | Tensile Strength | Dimensional Stability | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinforced HDPE Geomembrane | Very High | Excellent | Dams, tunnels, critical containment |
| Standard HDPE Geomembrane | High | Good | Landfills, ponds |
| PVC Waterproof Membrane | Medium | Moderate | Building waterproofing |
Application Scenarios
Reinforced Waterproofing HDPE Geomembrane is specified by EPC contractors, engineering consultants, and developers in:
Water reservoirs and hydraulic structures
Landfill caps and hazardous waste containment
Tunnel and underground structure waterproofing
Mining tailings storage facilities
Industrial wastewater and chemical ponds
Core Engineering Pain Points and Solutions
High Hydraulic Pressure: Reinforcement layer improves pressure resistance
Subgrade Movement: Enhanced tensile stability limits deformation
Puncture Risk: Multi-layer structure increases puncture tolerance
Long-Term Aging: HDPE formulation ensures extended service life
Risk Warnings and Mitigation Measures
Improper seam welding → Use compatible extrusion or wedge welding methods
Reinforcement exposure → Ensure complete encapsulation during manufacturing
Subgrade irregularities → Install cushioning geotextiles where required
Thermal stress during installation → Control installation temperature range
Procurement and Selection Guide
Define project waterproofing and containment objectives
Evaluate hydraulic pressure and chemical exposure levels
Select appropriate thickness and reinforcement type
Confirm compliance with ASTM or ISO standards
Assess welding method compatibility
Review supplier quality control and test reports
Verify installation support and technical documentation
Engineering Case Example
In a municipal water reservoir project, a 2.0 mm Reinforced Waterproofing HDPE Geomembrane was installed beneath a concrete lining. The reinforced structure accommodated subgrade movement while maintaining watertight integrity under sustained hydrostatic pressure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What differentiates reinforced HDPE geomembrane from standard HDPE?
A: Added internal reinforcement for higher tensile stability.Q2: Is it suitable for high-pressure water applications?
A: Yes, reinforcement improves pressure resistance.Q3: Can it be welded onsite?
A: Yes, using standard HDPE welding equipment.Q4: Does reinforcement reduce flexibility?
A: Slightly, but remains suitable for engineered applications.Q5: What thickness is common for reservoirs?
A: Typically 1.5–2.5 mm.Q6: Is chemical resistance affected by reinforcement?
A: No, HDPE layers provide primary resistance.Q7: Can it be used under concrete linings?
A: Yes, commonly used as a composite lining system.Q8: What is the expected service life?
A: Over 50 years under buried conditions.Q9: Is UV resistance required during storage?
A: Yes, exposure time should be controlled.Q10: Does it meet international standards?
A: Typically compliant with ASTM and ISO requirements.
Call to Action
For project-specific quotations, detailed technical datasheets, compliance certificates, or engineering samples of Reinforced Waterproofing HDPE Geomembrane, please submit a formal inquiry to receive professional technical support.
E-E-A-T Author Credentials
This technical article is authored by geosynthetics and civil engineering specialists with more than 15 years of experience in waterproofing systems, geomembrane design, and EPC infrastructure delivery, ensuring accuracy, authority, and practical relevance.