Geosynthetic Needle Punched Nonwoven Geotextile Fabric
The geosynthetic industry has experienced substantial growth, driven by the rising need for sustainable infrastructure, effective soil stabilization, and efficient drainage systems. Geosynthetic needle punched nonwoven geotextile fabric has emerged as a critical solution in civil engineering projects, including roads, railways, retaining walls, and landscaping applications.
Market research indicates that the global nonwoven geotextile market is expected to surpass USD 6 billion by 2030, with needle punched variants capturing a significant share due to their superior mechanical strength and filtration performance. International buyers increasingly demand fabrics that provide long-term reliability, enhanced water permeability, and ease of installation.
Global Market Overview of Geosynthetic Needle Punched Nonwoven Geotextiles
The geosynthetic industry has experienced substantial growth, driven by the rising need for sustainable infrastructure, effective soil stabilization, and efficient drainage systems. Geosynthetic needle punched nonwoven geotextile fabric has emerged as a critical solution in civil engineering projects, including roads, railways, retaining walls, and landscaping applications.
Market research indicates that the global nonwoven geotextile market is expected to surpass USD 6 billion by 2030, with needle punched variants capturing a significant share due to their superior mechanical strength and filtration performance. International buyers increasingly demand fabrics that provide long-term reliability, enhanced water permeability, and ease of installation.
Technical Specifications and Product Structure
Needle punched nonwoven geotextile fabrics are composed of high-quality polypropylene or polyester fibers mechanically interlocked to create a uniform, porous sheet. Key technical parameters typically include:
• Fabric weight: 100–500 g/m²
• Thickness: 2–6 mm
• Tensile strength: 30–60 kN/m
• Elongation at break: 50–100%
• Puncture resistance: ≥ 500 N
• Water permeability: ≥ 100 L/m²/s
The multi-layered and dense needle-punched structure provides excellent soil filtration, separation, and reinforcement capabilities. Heavier fabric weights are used for high-load applications, while lighter variants serve for landscaping and erosion control.
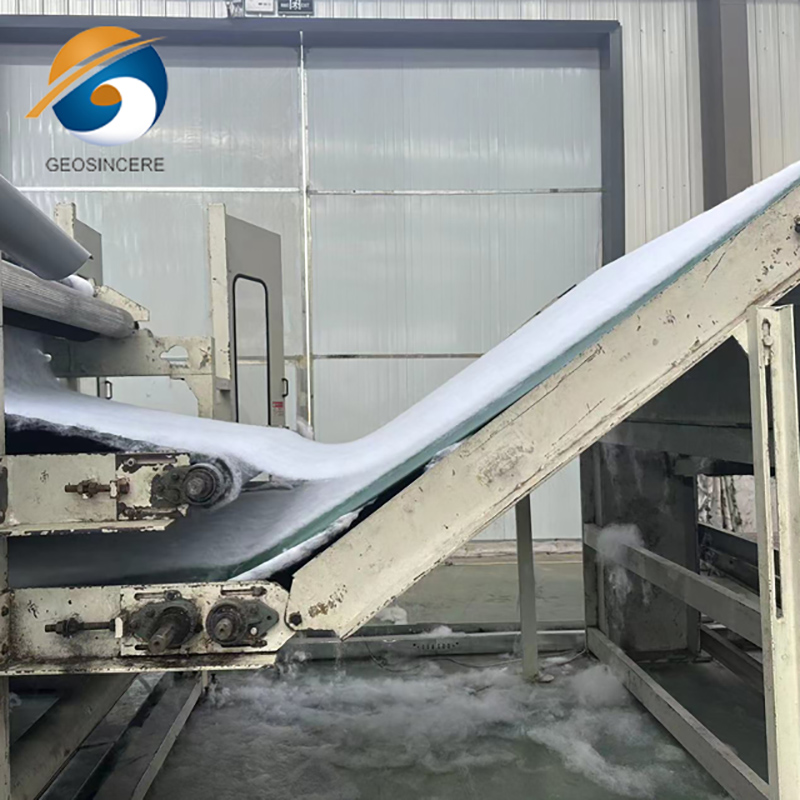
Manufacturing Process and Quality Control
The manufacturing process of geosynthetic needle punched nonwoven geotextiles involves blending synthetic fibers, forming a fiber web, and then mechanically bonding them using needle punching. This ensures uniform thickness, high tensile strength, and consistent porosity.
Quality assurance includes rigorous testing for tensile strength, elongation, permeability, puncture resistance, and UV stability. Compliance with ASTM, ISO, and EN standards is critical to meet international buyer requirements and guarantee long-term performance in varied environmental conditions.
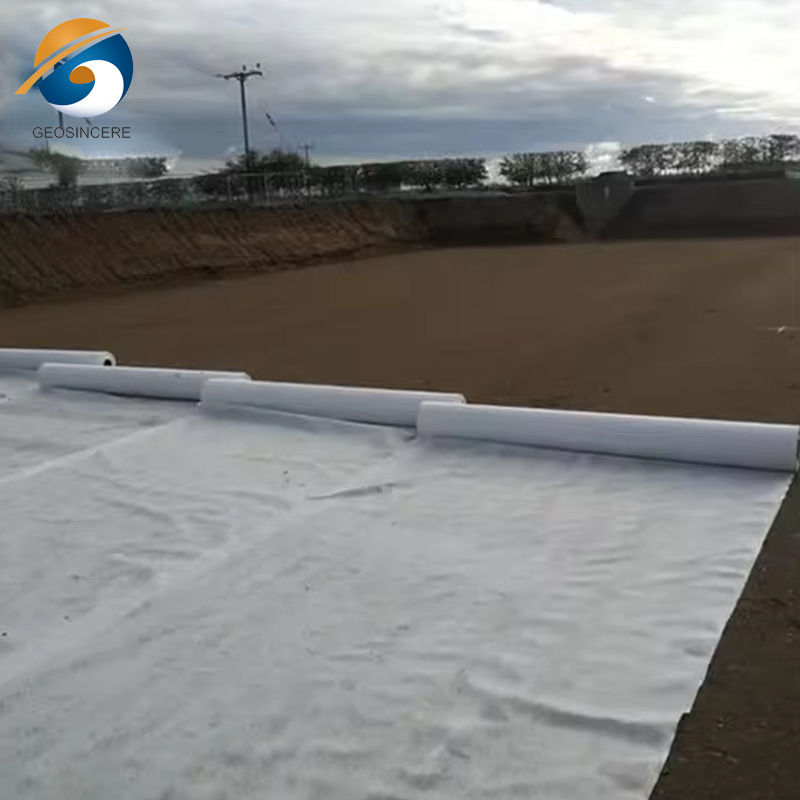
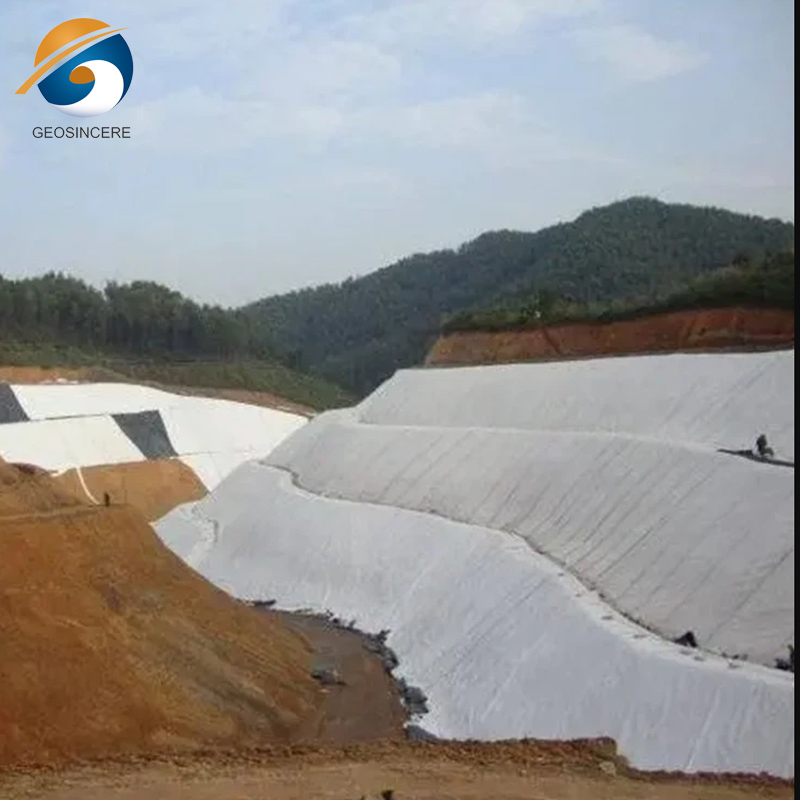
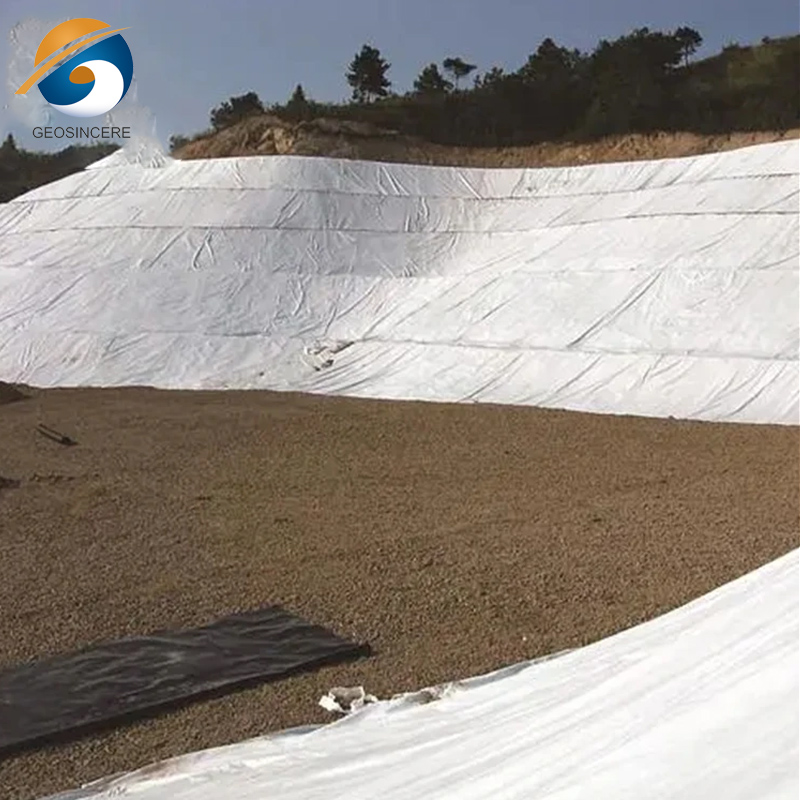
Applications in Civil Engineering and Infrastructure
Geosynthetic needle punched nonwoven geotextile fabrics serve multiple functions in civil and environmental engineering projects:
• Road base stabilization and subgrade reinforcement
• Railway track bedding and ballast separation
• Drainage and filtration systems
• Retaining walls and slope stabilization
• Erosion control and landscaping applications
The fabric’s ability to separate soil layers while allowing water flow prevents clogging and improves soil durability. In large-scale infrastructure projects, these geotextiles reduce maintenance costs and extend the service life of constructed assets.
Market Trends and Buyer Preferences
International buyers prioritize durability, environmental compliance, and ease of installation. Geosynthetic fabrics with UV resistance, high tensile strength, and proven filtration efficiency are increasingly favored. Buyers also value pre-cut rolls and customizable dimensions to suit specific project requirements, as this reduces on-site labor and installation time.
Additional considerations include detailed technical documentation, certifications, and supplier support for installation guidance. Suppliers offering these services alongside reliable logistics and competitive pricing tend to secure long-term partnerships with global engineering and construction firms.
Pricing Considerations
Pricing of geosynthetic needle punched nonwoven geotextile fabric depends on fiber type, fabric weight, thickness, and production scale. Typical price ranges from USD 1 to 4 per square meter depending on specifications and volume. While cost is a factor, buyers prioritize durability and long-term performance to minimize lifecycle costs and prevent infrastructure failures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the expected lifespan of needle punched nonwoven geotextile fabric?
With proper installation, the fabric can last 15–25 years under normal environmental conditions.
2. Can the fabric be customized for specific project needs?
Yes. We provide custom weights, thicknesses, and roll sizes tailored to project requirements.
3. How does the fabric enhance drainage and filtration?
Its needle-punched structure maintains high porosity, efficiently filtering soil particles while allowing water flow.
4. What technical documentation is provided for international buyers?
We provide comprehensive test reports, certifications, and datasheets compliant with ASTM, ISO, and EN standards.
Professional Consultation and Sample Requests
For contractors, civil engineers, and procurement professionals seeking reliable geosynthetic solutions, our geosynthetic needle punched nonwoven geotextile fabric offers superior performance in filtration, drainage, and soil stabilization. Contact our technical team to request detailed specifications, competitive quotations, and material samples tailored to your project needs.
We are committed to delivering certified, high-quality geotextile solutions that improve infrastructure longevity, enhance drainage efficiency, and support sustainable construction practices worldwide.