HDPE Polythene Sheet Fish Pond Rubber Tank Liner
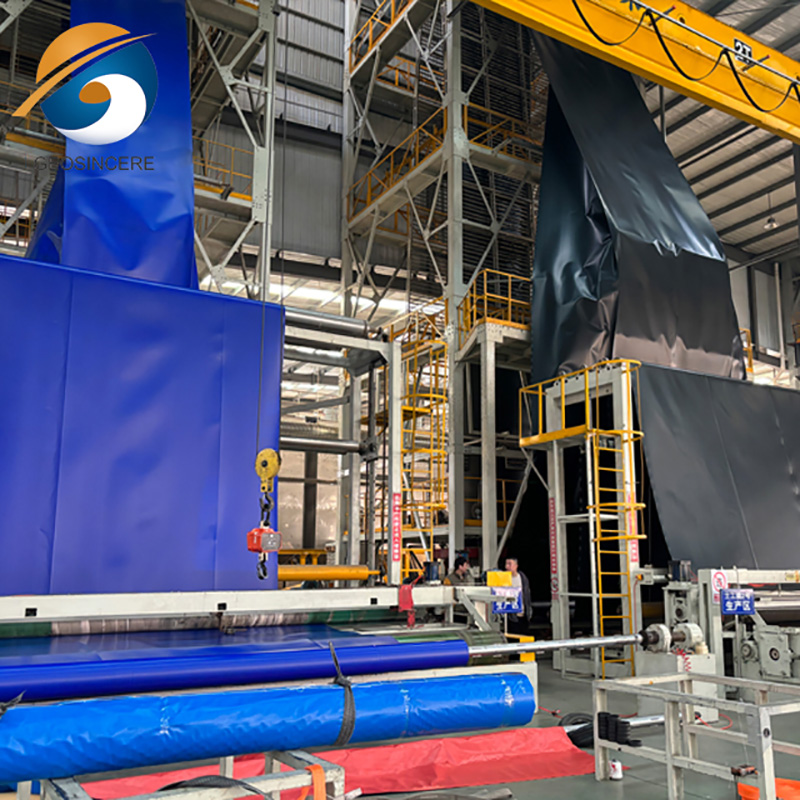
Manufacturing Process
Resin Blending: HDPE pellets mixed with carbon black and stabilizers in an automated batching system.
Extrusion: Single or double extrusion lines melt and extrude the compound into uniform sheets.
Calendering: Rollers shape the membrane to precise thickness and width.
Surface Treatment: Texturing applied through patterned rollers when required.
Cooling and Stabilization: Controlled cooling prevents shrinkage and internal stress.
Quality Inspection: Includes tensile strength tests, hydrostatic pressure tests, pinhole detection, and dimensional checks.
HDPE Polythene Sheet Fish Pond Rubber Tank Liner Definition
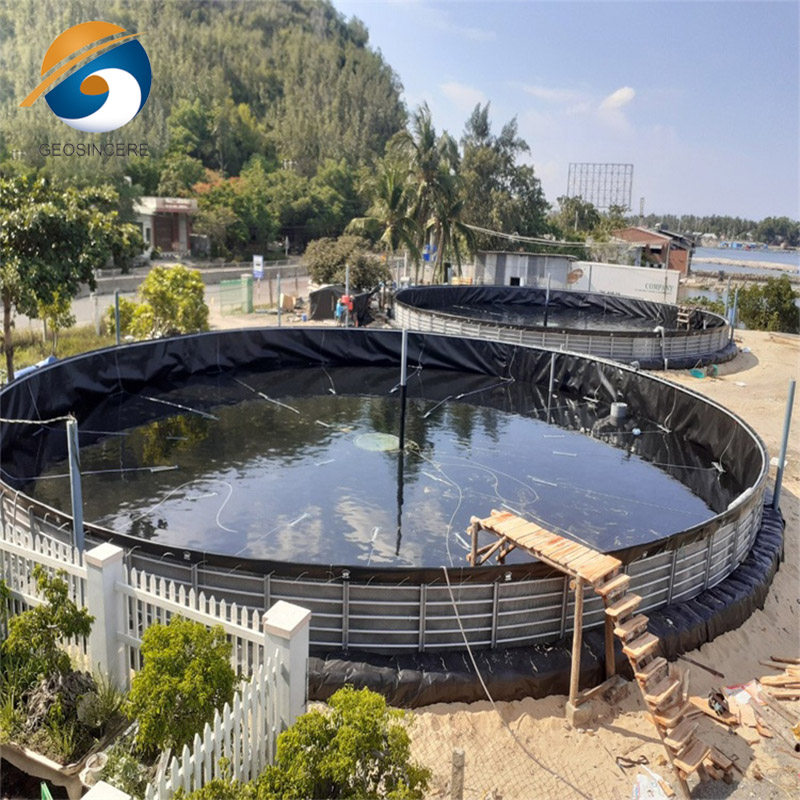
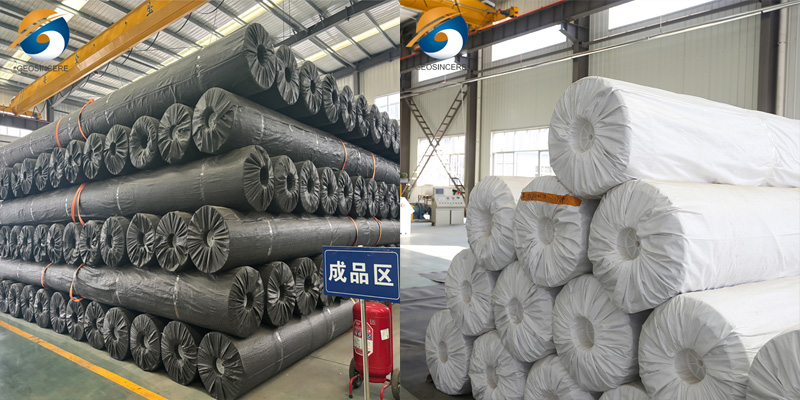
HDPE Polythene Sheet Fish Pond Rubber Tank Liner is a geomembrane designed to provide long-term waterproofing, chemical stability, and structural containment for aquaculture ponds, rubber tank systems, and engineered water reservoirs. It offers superior leak resistance, environmental protection, and operational durability.
Technical Parameters and Specifications
| Parameter | Specification Range |
|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.5–1.5 mm |
| Density | ≥ 0.94 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 20–27 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ≥ 500%–700% |
| Puncture Resistance | ≥ 650–1200 N |
| Carbon Black Content | 2.0%–3.0% |
| Water Absorption | < 0.01% |
| Expected Service Life | 10–20 years depending on UV exposure |
| Temperature Range | -35°C to +55°C |
Structure and Material Composition
Primary HDPE Layer: High-density resin ensuring water impermeability.
Carbon Black Stabilizer: Enhances UV resistance and outdoor durability.
Antioxidant Additives: Prevent thermal degradation during long-term exposure.
Molecular Orientation Layer: Improves mechanical strength and tear resistance.
Optional Textured Surface: Increases friction on sloped pond walls.
Manufacturing Process
Resin Blending: HDPE pellets mixed with carbon black and stabilizers in an automated batching system.
Extrusion: Single or double extrusion lines melt and extrude the compound into uniform sheets.
Calendering: Rollers shape the membrane to precise thickness and width.
Surface Treatment: Texturing applied through patterned rollers when required.
Cooling and Stabilization: Controlled cooling prevents shrinkage and internal stress.
Quality Inspection: Includes tensile strength tests, hydrostatic pressure tests, pinhole detection, and dimensional checks.
Industry Comparison
| Material | Lifespan | Chemical Resistance | Flexibility | Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE Polythene Sheet | 10–20 years | Excellent | Moderate | Medium |
| PVC Pond Liner | 6–10 years | Good | High | Low |
| EPDM Rubber Liner | 12–15 years | Medium | Very High | High |
| LDPE Film | 3–6 years | Poor | High | Very Low |
Application Scenarios
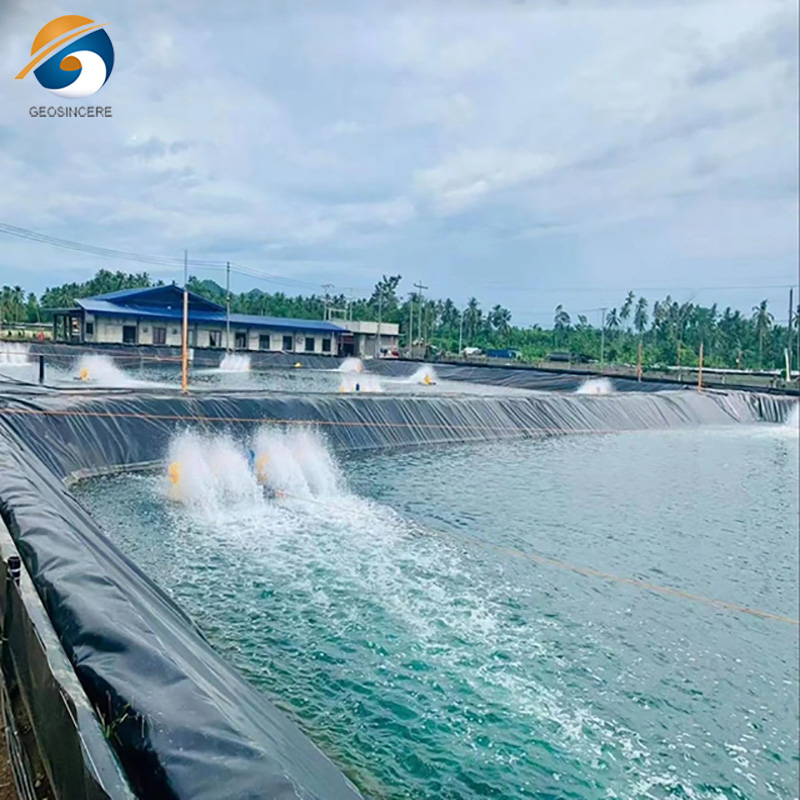
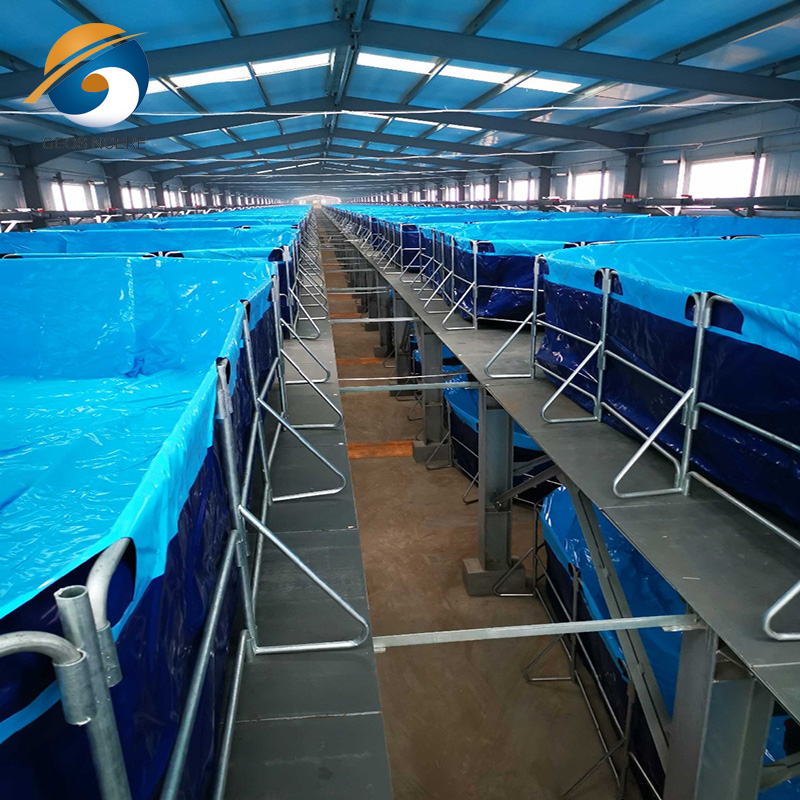
Aquaculture Projects: Intensive fish farming ponds and shrimp tanks.
Rubber Tank Systems: Prefabricated tank linings for modular farming systems.
Agricultural Water Storage: Irrigation ponds and farm reservoirs.
EPC Engineering Projects: Landscape water features, wastewater channels.
Distributors and Importers: Supply to farm contractors, pond builders, and project developers.
Core Pain Points and Engineering Solutions
Leak Risk from Soil Settlement: HDPE membrane provides a continuous waterproof barrier independent of soil movement.
Algae and Bacteria Growth: Smooth HDPE surfaces reduce microbial adhesion.
UV Damage in Outdoor Farms: Carbon black stabilizers extend service life under strong sunlight.
Poor Mechanical Strength in Budget Liners: Reinforced HDPE structure improves tear and puncture resistance.
Risk Warnings and Preventive Recommendations
Sharp objects beneath the liner can cause punctures—install geotextile padding.
Improper welding creates seam failures—use trained welders and calibrated equipment.
Long-term direct sunlight accelerates aging—select higher carbon black content for tropical regions.
Incorrect pond grading may create liner tension points—ensure proper slope and foundation leveling.
Procurement and Selection Guide
Identify the type of pond or tank (fish pond, rubber tank, irrigation reservoir).
Determine required thickness based on water depth and project size.
Check mechanical performance values (tensile strength, puncture resistance).
Request product certifications (ISO standards, ASTM testing reports).
Evaluate UV exposure level and select suitable stabilizer formulation.
Confirm welding method compatibility and installation accessories.
Review supplier’s engineering case history and technical support capability.
Engineering Case Study
A commercial aquaculture farm constructed a 2,000 m² intensive fish pond requiring stable waterproofing and long-term durability. A 1.0 mm HDPE Polythene Sheet Fish Pond Rubber Tank Liner was selected. The EPC contractor installed a non-woven geotextile buffer, positioned HDPE sheets using mechanical rollers, and welded seams with automated hot-wedge equipment. Quality checks included vacuum box testing and destructive seam sampling. The pond achieved zero leakage during 48-hour hydrostatic testing and has remained in stable operation for three production cycles.
FAQ
What thickness is recommended for fish ponds? — 0.75–1.0 mm for most applications.
Can the liner be used for drinking-water ponds? — Only if certified for potable-water use.
How long can HDPE liner last outdoors? — Typically 10–20 years depending on UV exposure.
Is welding required? — Yes, for a continuous waterproof system.
Can it be installed over rough soil? — A geotextile buffer layer is required.
Is it safe for aquaculture species? — Yes, HDPE is chemically inert.
How is damage repaired? — Use hot-air welding patches.
Can the liner withstand sharp fish fins? — Yes, with proper puncture resistance selection.
Is textured surface necessary? — Useful for steep banks to increase friction.
What tests are required on-site? — Air channel, vacuum box, and visual inspections.
Request a Quote / Technical Data / Engineering Sample
To obtain detailed technical data, project-specific quotations, or engineering samples of HDPE Polythene Sheet Fish Pond Rubber Tank Liner, please contact our professional engineering support team. We provide specification sheets and customized selection guidance for industrial and aquaculture applications.
E-E-A-T Author Credentials
This article is prepared by a senior geomembrane engineer with 10+ years of experience in aquaculture pond systems, waterproofing materials, and industrial reservoir design. All technical details follow internationally recognized standards and verified engineering practices.