What is PP Geogrid?
In civil engineering, geotechnical solutions, and modern construction, one material has been a key factor in stability, durability, and cost-efficiency: PP Geogrid. If you work on infrastructure projects, landscaping, or soil reinforcement, you must know this versatile geosynthetic. This all-inclusive guide explains what PP geogrid is, its various uses, the substantial advantages it brings, and the crucial specifications that characterize its performance.
1. Understanding PP Geogrid: The Basics
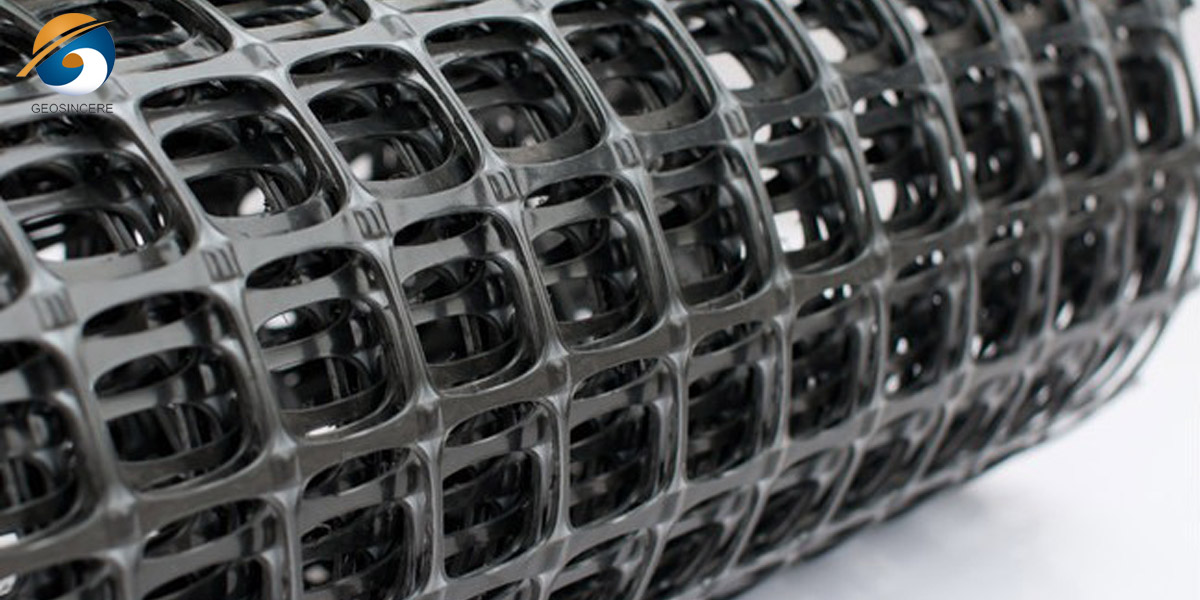
PP geogrid is a geosynthetic material derived from polypropylene (PP), a high-grade thermoplastic polymer. "Geogrid" indicates its open, grid-like structure, usually produced by stretching a punched polypropylene sheet in both the longitudinal and transverse directions—a method named biaxial orientation. As a result, a network of fully connected ribs with large, regular apertures is formed.
The key concept of PP geogrid is that it provides tensile strength. Unlike soil, which is strong when compressed but weak when stretched, the geogrid has a high tensile strength. Upon embedding in soil or aggregate, the geogrid meshes with the particles through the apertures, thus creating a mechanically stabilized composite zone. This working combination, known as interlock, keeps the fill material in place, facilitates load distribution over a larger area, and thereby, substantially enhances the structural strength of the soil mass.
2. PP Geogrid Key Manufacturing Processes: The Secret to Its Strength
The characteristics of PP geogrid largely depend on how it's made:
2.1 Extrusion and Punching
Polypropylene resin is softened by heat and formed into a sheet through an extrusion process, which is later patterned with holes through precision punching.
2.2 Stretching (Orientation)
The sheet with holes is subjected to heat and stretched in both the machine (longitudinal) and cross (transverse) directions simultaneously. This molecular orientation lining up polymer chains dramatically increases the tensile strength and stiffness of the ribs creating the final grid pattern.
2.3 Finishing
The product may be coated or treated for additional properties, such as enhanced UV resistance for long-term exposed applications.
The end result is a biaxial geogrid; thus, it's characterized by a high tensile strength in both principal directions, which makes it a perfect choice for stabilizing planar areas like roadbeds and foundations.
3. Main Uses of PP Geogrid
Due to its several advantages, PP geogrid has been extensively used in engineering projects. It functions as a separator, reinforcer, and stabilizer in engineering projects.
3.1 Roadway and Pavement Construction
This is probably the top use of the material. In the construction of roads (unpaved and paved), railway tracks, and airport runways, PP GEOGRID is set between the subgrade soil and the base aggregate layer.
3.1.1 How it Works
The PP polypropylene geogrid acts as a barrier that stops soft subsoil and strong aggregate from mixing (separation). Moreover, the base course is reinforced, thanks to the PP GEOGRID that helps in load distribution and in lessening rutting and deformation of the surface.
3.1.2 Outcome
The lifespan of the pavement is prolonged; less aggregate thickness is needed (which means savings on material costs), and there is an enhanced performance on weak subgrades.
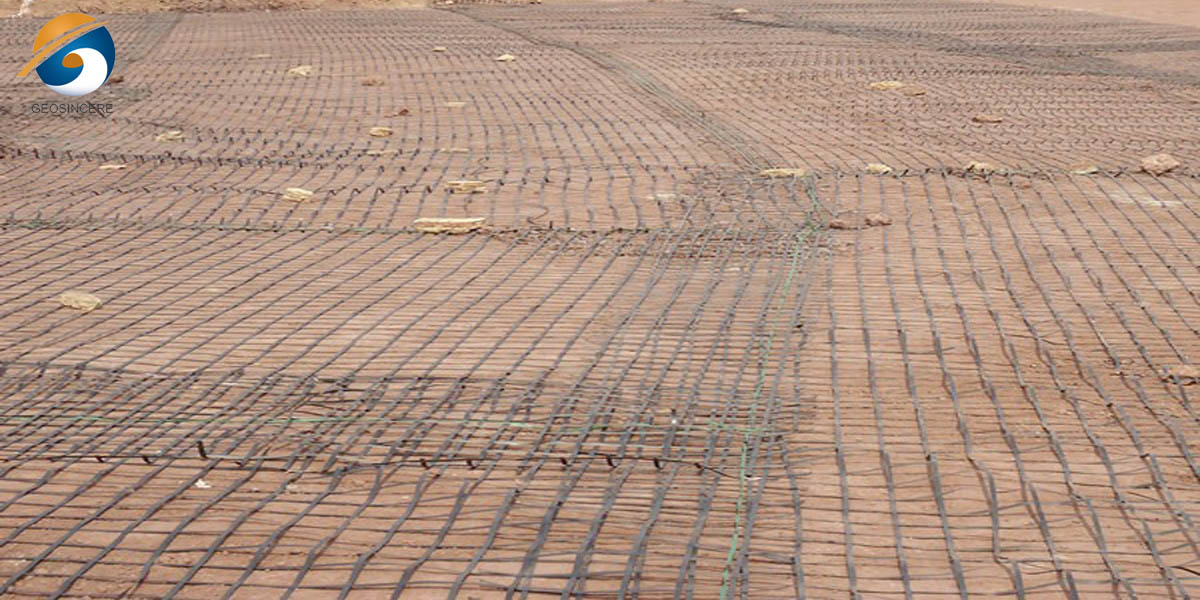
3.2 Retaining Walls and Steep Slopes
PP geogrid is a great option to use when making Mechanically Stabilized Earth (MSE) walls and reinforced soil slopes.
3.2.1 Mechanism
Polypropylene geogrid sheets are placed at intervals horizontally between compacted soil lifts. The backfilled or native soil gets locked to the grid, so a single, cohesive, gravity-retaining mass is formed which can resist high lateral earth pressures.
3.2.2 Result
Such a design approach allows the erection of almost vertical retaining walls and the posing of steeper slopes that would otherwise not be possible in natural soil, thus right-of-way acquisition has been minimized. These types of works can be executed in less time and usually at a lower cost when compared with concrete retaining walls.
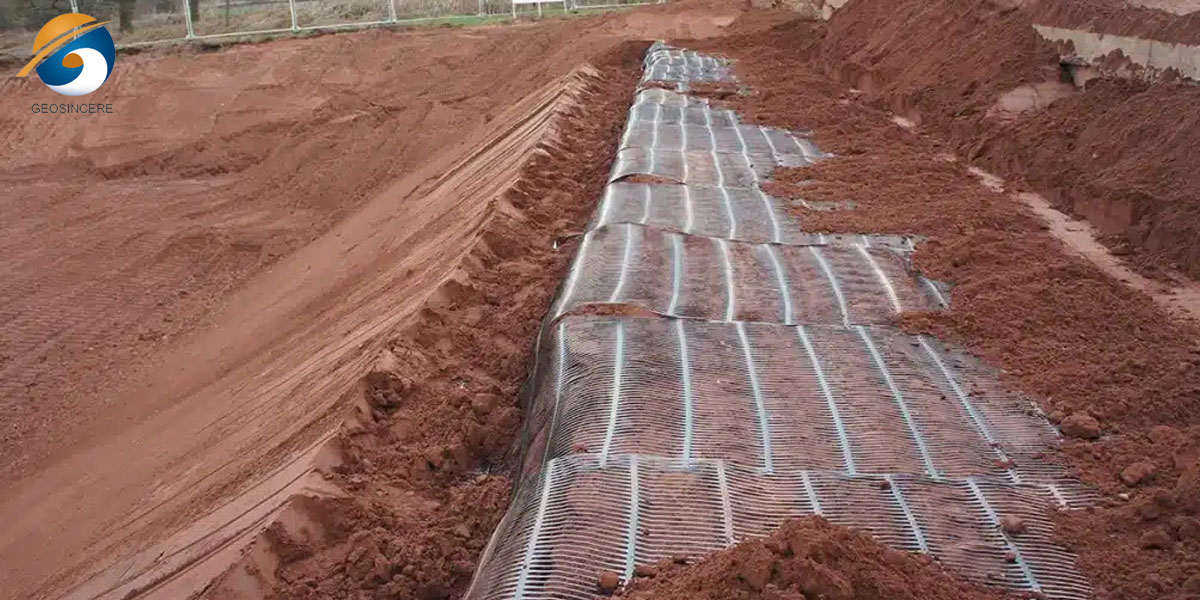
3.3 Foundation and Embankment Support
The biggest challenge in construction of embankments and foundations in very soft, compressible soils (such as peat or soft clay) is that the build-up is extremely difficult.
3.3.1 Mechanism
Before placing the fill over a soft subgrade, one or multiple layers of biaxial polypropylene geogrid is positioned. Being a tensioned membrane, the geogrid provides a bridging effect and load distribution features apart from other benefits improving the bearing capacity.
3.3.2 Result
Such a measure has raised the level of global stability, lowered differential settlement, and has averted cases where expensive deep foundation techniques or soil replacement would be used.
3.4 Landfill and Erosion Control Systems
3.4.1 Landfill Liners/Caps
PP biaxial geogrid application in landfill covers has been to provide structural reinforcement for soil covers over landfill caps and drainage layers so that the stability of slopes is ensured.
3.4.2 Erosion Control
Where slopes have a risk of losing their topsoil by surface erosion, geogrids offer the possibility of securing erosion control mats or vegetated systems thus providing an instant stability that lasts until the vegetation grows.
4. Major Benefits of Using PP Geogrid
Here are some of the key benefits that came with the introduction of PP geogrid:
4.1 Superior Cost-Effectiveness
The solution has oftentimes proved to be the cheapest one among the options of ground stabilizing measures. The supply and haulage costs get significantly cut down with the help of it since reduced aggregate base course thickness (by 30% and more) gets made feasible and the use of on-site or lower quality fill keeps getting allowed.
4.2 Enhanced Structural Performance and Longevity
Structures strengthened with geogrid have been demonstrated to have lower incidence of rutting, cracking, and settlement. Thus, maintenance works on the roads, retaining walls, and foundations become less frequent and the design life gets extended.
4.3 Rapid Construction
The installation process is straightforward and speedy. Rolls of geogrid weigh very little, are very easy to handle, and can be unrolled quickly, thus project schedules get significantly shortened as compared to the wet construction methods.
4.4 Environmental Sustainability
PP geogrid offers a nod to green construction in that it:
- Drastically reduces the need for the quarrying and consumption of natural aggregates.
- Makes the use of marginal soils possible, which, in turn, lessens the import/export of fill materials.
- Reduces the carbon footprint resulting from the transport and compaction of materials.
4.5 Excellent Durability and Chemical Resistance
Polypropylene is a practically inert polymer and is highly resistant to attack from the majority of soils, chemicals, and biologically related degradation. By being adequately compounded with carbon black for UV protection, a design life of over 100 years in many buried applications could be achieved.
4.6 Versatility and Adaptability
Given that it is biaxially strong, almost any project kind can take advantage of it and no site condition is too difficult, be it a highway project or a residential driveway.
5. PP Geogrid Critical Specifications and Properties Explained
Selecting the appropriate PP geogrid for a specific engineering project requires a thorough understanding of its key technical specifications, which are quantified through standardized test methods (such as ASTM or ISO). These properties define its performance and suitability. The most fundamental characteristic is its Tensile Strength, measured in kilonewtons per meter (kN/m). Since geogrid mesh is a biaxial product, this strength is evaluated in both the Machine Direction (MD)—the direction of manufacture—and the Cross Machine Direction (CMD). This bidirectional strength is the core property that allows the grid to distribute loads and reinforce soil planes effectively. Closely related is the Strain at Peak Load, expressed as a percentage (%), which indicates the material's ductility or how much it can elongate before reaching its maximum strength. A balanced strength-to-strain relationship is crucial for predictable performance.
The geometric design of the grid is equally important. The Aperture Size, typically given in millimeters (e.g., 25mm x 25mm), defines the openings between the ribs. This size must be carefully chosen to achieve optimal interlock with the specific soil or aggregate particle size used in the project. The integrity of the grid's structure hinges on its Junction Strength, which is the strength of the points where the ribs intersect. A high junction strength, often expressed as a percentage of the rib strength or in force units (Newtons), is critical to prevent rib detachment under load. Furthermore, Aperture Stability (or rib stability) measures the grid's ability to maintain its geometric shape under in-service stresses, ensuring the long-term effectiveness of the soil-interlock mechanism.
For long-term durability, two polymer-specific properties are paramount. First, Creep Behavior refers to the tendency of a polymeric material to slowly deform under a constant, sustained load. High-quality PP geogrid is engineered from specially formulated polypropylene to exhibit low creep characteristics, ensuring that its reinforcing function does not diminish significantly over decades. Second, for applications where the geogrid may be exposed to sunlight during construction or in its final service life, UV Resistance is vital. This is typically achieved by incorporating 2-3% carbon black into the polymer, which acts as a stabilizer, protecting the molecular chains from photo-oxidative degradation and preserving the material's mechanical properties.
A critical engineering principle must be emphasized: the ultimate tensile strength derived from short-term tests is not used directly in final design. Instead, engineers apply a series of partial reduction factors to account for potential installation damage, long-term creep, and chemical/biological environments. Applying these factors to the ultimate strength yields the Long-Term Design Strength (LTDS), which is the conservative, safe strength value used in all stability calculations and safety factor analyses. Understanding and specifying these properties ensures that the selected PP geogrid will perform reliably throughout the intended design life of the structure.
6. PP Geogrid Installation Best Practices
Even the best geogrid requires proper installation:
6.1 Subgrade Preparation
The surface must be graded, compacted, and free of sharp protrusions, standing water, and debris.
6.2 Unrolling and Placement
Rolls are deployed manually or mechanically, placed with the strong direction (usually the roll length) oriented perpendicular to the primary traffic direction or along the slope contour.
6.3 Overlap and Connection
Adjacent rolls must be overlapped (typically 0.3m to 1.0m, as per specification) or connected with tying bars or plastic ties. At walls, the geogrid must be adequately connected to the facing units.
6.4 Backfilling and Compaction
Fill material is placed and spread in thin lifts before compaction. Equipment should not directly operate on the exposed geogrid. The first lift is often placed and spread by lightweight machinery or manually.
Conclusion
Shandong Geosino New Material Co., Ltd. (GEOSINCERE Geosynthetics) PP geogrid is far more than just a plastic mesh; it is a high-strength, engineered polymer solution that revolutionizes how we build on and with soil. By providing efficient tensile reinforcement, it solves age-old problems of soil weakness, leading to more robust, durable, and economical infrastructure. From highways and retaining walls to working platforms on soft ground, its applications are a testament to its versatility.
Understanding its uses, benefits, and critical specifications—such as tensile strength, aperture size, junction strength, and long-term design properties—is essential for engineers, contractors, and project owners to select the right product and ensure a successful, long-lasting project. As construction trends continue to emphasize speed, sustainability, and cost-efficiency, the role of PP geogrid as a foundational geosynthetic is set to become even more prominent.