Non Woven Geotextile Filter Fabric Drainage Underlayment
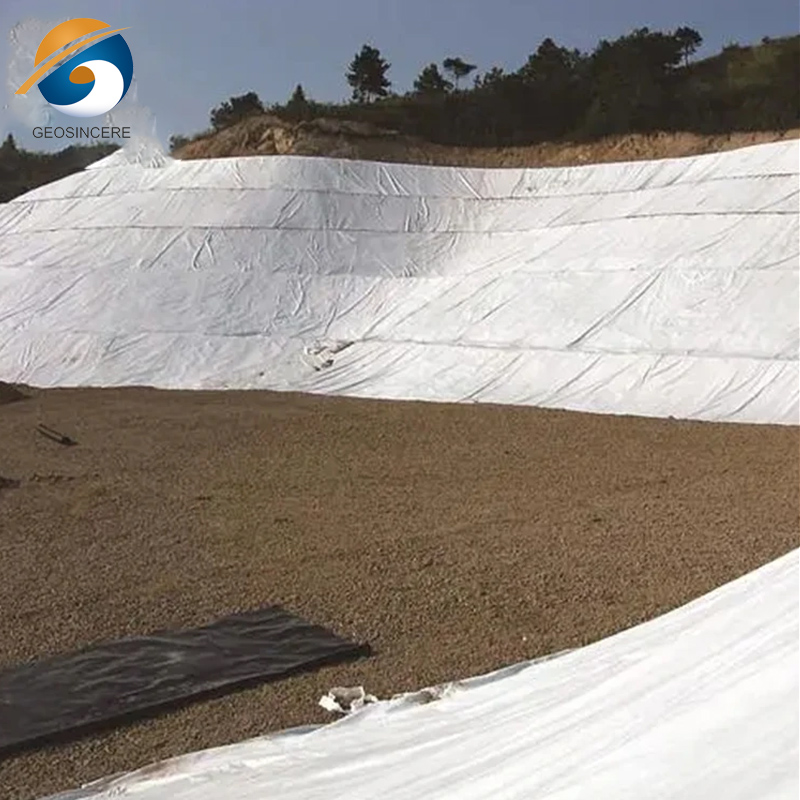
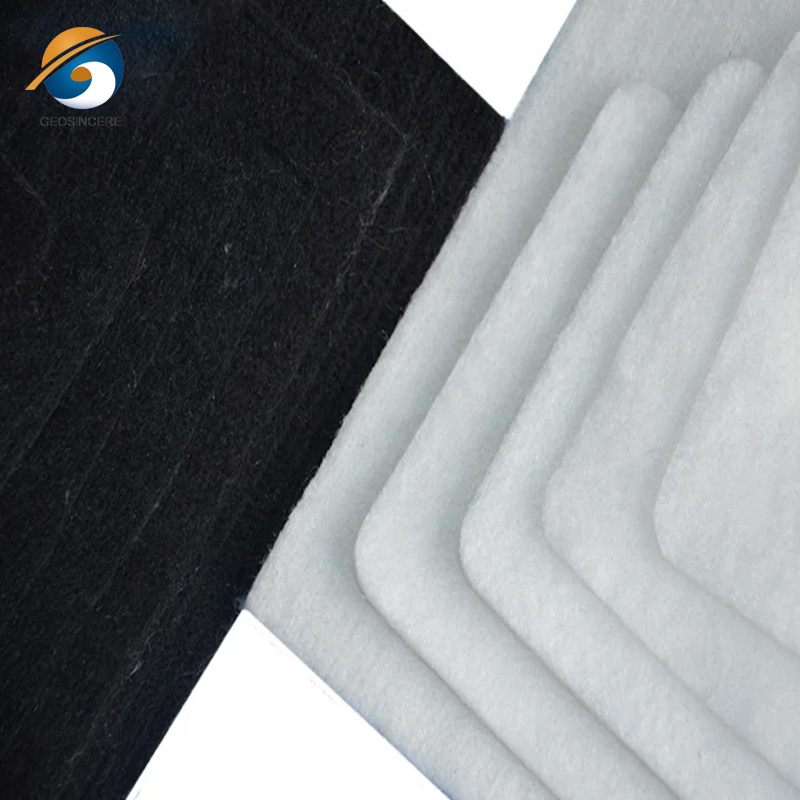
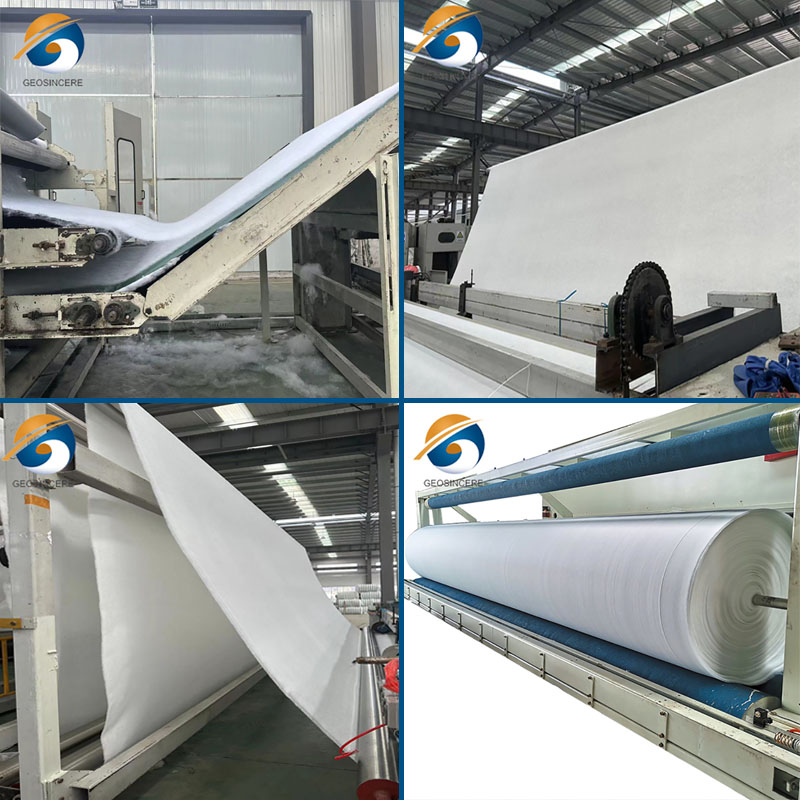
Non-woven geotextile filter fabric drainage underlayment refers to a specific type of geotextile material that is used to provide filtration and drainage functions in various construction and geotechnical applications. Non-woven geotextiles used as filter fabric underlayment are characterized by a random arrangement of synthetic fibers that are mechanically bonded together. This structure provides the geotextile with high permeability, strength, and filtration efficiency.
Non-woven geotextile filter fabric acts as a filter by allowing water to pass through while preventing the migration of fine soil particles. It helps to maintain the long-term effectiveness of drainage systems by preventing clogging and ensuring efficient water flow.The underlayment geotextile helps to enhance the drainage capacity of the system by providing a pathway for water to freely move through the soil and into the drainage system.
Non woven geotextile filter fabric plays a critical role in modern civil engineering and landscape construction, particularly as a drainage underlayment material. Engineered from polypropylene or polyester fibers, it provides filtration, separation, and drainage in roadways, retaining walls, landfills, and sub-surface water systems.
This article presents a detailed technical guide to non woven geotextile filter fabric for drainage applications. We will cover its composition, installation techniques, compliance with international standards, material properties, engineering rationale, and common use cases—equipping contractors, engineers, and infrastructure planners with precise and actionable knowledge.
What Is Non Woven Geotextile Filter Fabric?
Non woven geotextiles are needle-punched or heat-bonded fabrics designed to manage the flow of water while preventing the migration of fine soil particles. Unlike woven geotextiles, these fabrics lack a regular weave pattern, offering high permeability and filtration capabilities.
Key Functions:
Filtration – Allows water to pass while retaining soil
Drainage – Channels water laterally along the underlayment
Separation – Prevents mixing of different soil layers
Protection – Shields geomembranes from puncture
Material Composition and Performance Properties
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material | Polypropylene (PP) or Polyester (PET) |
| Thickness | 0.8 mm – 6.0 mm (varies by grade) |
| Tensile Strength | 8–50 kN/m (ASTM D4595) |
| Elongation at Break | 40–80% (ASTM D4632) |
| Permittivity | ≥ 0.7 s⁻¹ (ASTM D4491) |
| Water Flow Rate | ≥ 100 gpm/ft² (ASTM D4491) |
| Apparent Opening Size | 0.15 – 0.3 mm (ASTM D4751) |
| UV Resistance | ≥ 70% strength retained after 500 hours (ASTM D4355) |
Compliance with Industry Standards
To ensure structural integrity and performance, non woven geotextiles must adhere to the following global standards:
| Standard | Governing Body | Application Area |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM D4759 | ASTM International | Geotextile specification conformity |
| ISO 10318 | International Standards Org. | Geotextile classification and properties |
| AASHTO M288 | American Association of State Highway & Transportation Officials | Road construction and drainage |
| EN 13252 | European Standard | Drainage layer geotextiles |
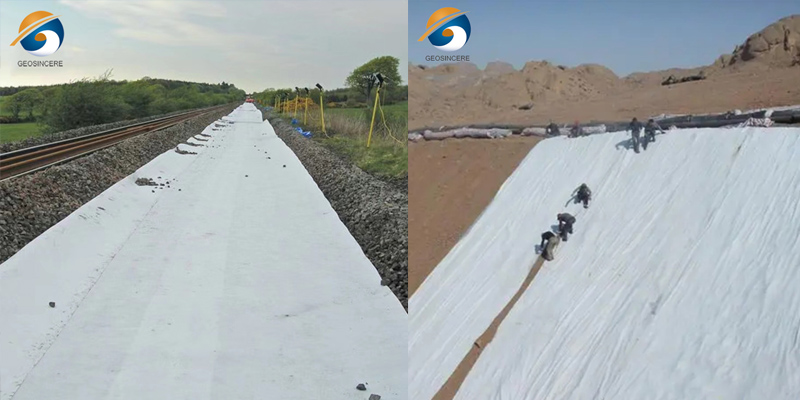
Applications in Drainage Underlayment
1. French Drains & Trench Drains
Wraps around perforated drainage pipes
Allows high water flow while blocking fine particles
2. Retaining Wall Drainage
Installed between soil and wall to prevent hydrostatic pressure
Prolongs wall stability and prevents waterlogging
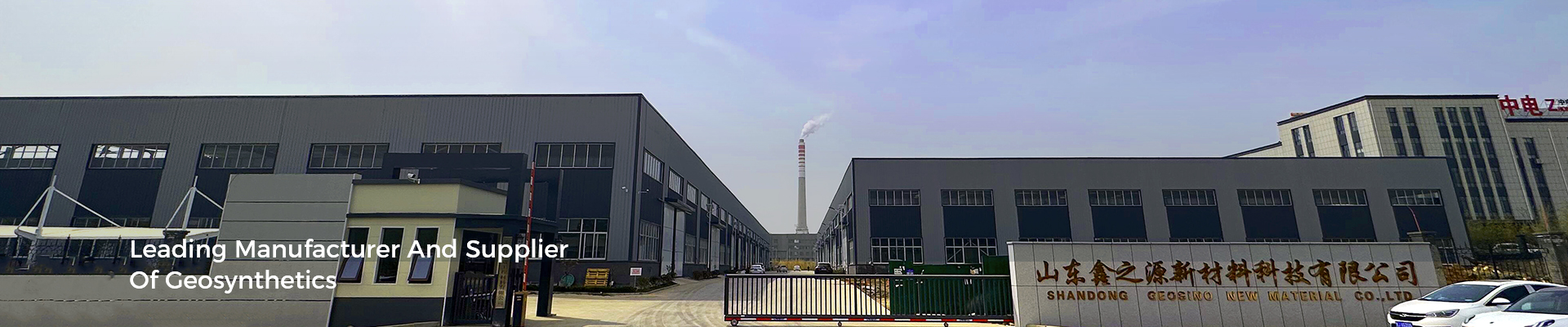
3. Under Riprap and Gabion Installations
Prevents erosion and migration of base soils
Maintains structural performance over time
4. Green Roofs and Planters
Facilitates drainage in confined horticultural systems
Supports plant health while preventing soil loss
Installation Guidelines
Site Preparation
Grade and compact the subgrade to ensure stability
Remove debris, sharp rocks, and vegetation
Fabric Placement
Unroll geotextile flat and without tension
Overlap adjacent sheets by 300–600 mm (12–24 inches), depending on soil conditions and slope
Anchoring & Securing
Use U-pins or ballast to hold fabric in place
Avoid wrinkles or folds that can impede water flow
Backfilling
Place gravel or sand layer gently to avoid damage
Compact as required without displacing the geotextile
Tip: Always install with the water flow direction perpendicular to the plane of the geotextile for optimal filtration performance.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
| Mistake | Issue Caused | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Inadequate overlap | Soil migration at seams | Maintain industry-specified overlaps |
| Using woven fabric for filtration | Clogging or insufficient flow | Use non woven fabrics for high permeability |
| Skipping edge anchoring | Fabric displacement under load | Secure all edges with staples or gravel |
| Incorrect opening size | Soil loss or clogging | Match AOS to project’s soil gradation curve |
FAQs: Non Woven Geotextile Fabric for Drainage
Q1: How is non woven geotextile different from woven geotextile?
Non woven fabric has higher permeability and better filtration, while woven fabrics provide higher tensile strength. Non woven is preferred for filtration and drainage, woven for stabilization and reinforcement.
Q2: Can I use non woven geotextile under gravel driveways?
Yes. It is ideal for separating gravel from soil and promoting subsurface drainage, extending the life of driveways and reducing rutting.
Q3: How long does non woven geotextile last?
When properly installed and UV-protected, high-quality polypropylene non woven geotextiles can last 20–50 years, depending on soil chemistry and application.
Q4: Is geotextile fabric permeable?
Yes. It allows water to pass while trapping soil particles—making it effective for filtering and draining.
Summary Table: Choosing the Right Non Woven Fabric
| Application | Recommended Weight | Opening Size (AOS) | Permittivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| French Drain | 4–6 oz/yd² | 0.21–0.25 mm | ≥ 1.0 s⁻¹ |
| Retaining Wall Drainage | 6–8 oz/yd² | 0.15–0.21 mm | ≥ 0.7 s⁻¹ |
| Road Underlayment | 8–10 oz/yd² | 0.15 mm | ≥ 0.5 s⁻¹ |
| Erosion Control | 6–10 oz/yd² | 0.21–0.30 mm | ≥ 0.7 s⁻¹ |
Final Action Call
Installing a non woven geotextile filter fabric for drainage underlayment is a strategic investment in long-term infrastructure performance. Whether you're building a retaining wall, a drainage trench, or a stable foundation for hardscape, this technical solution ensures water control, soil separation, and erosion resistance—all in one layer.
👉 Need help selecting the right grade or thickness?
Reach out to this site for free technical support, detailed specifications, and sample sheets tailored to your project.
The underlayment serves as a drainage layer, allowing water to flow freely through the geotextile while preventing the migration of soil particles. It helps to remove excess water from the site, preventing the buildup of hydrostatic pressure and promoting efficient drainage. Non-woven geotextiles have a random arrangement of fibers that creates a three-dimensional structure. This structure provides the fabric with excellent filtration and drainage properties. The non-woven structure also offers high tensile strength and puncture resistance.
Non-woven geotextile filter fabric drainage underlayment is typically made from synthetic materials such as polypropylene or polyester. These materials are chosen for their durability, resistance to biological degradation, and chemical stability.
High strength and durability
Lightweight and easy to handle
Resistance to biological degradation and chemical deterioration
Good filtration properties
Cost-effective compared to traditional construction methods
Applications of Non Woven Geotextile Filter Fabric Drainage Underlayment
Non-woven geotextile filter fabric drainage underlayment has a wide range of applications, including:
Subsurface drainage systems: It is commonly used beneath perforated pipes or gravel layers to enhance the drainage capacity of roadways, sports fields, retaining walls, and other structures.
Landfill and waste containment: Geotextile underlayment is applied beneath geomembranes in landfill applications to provide filtration and drainage, preventing the buildup of pore pressure and ensuring proper leachate collection and management.
Erosion control: Geotextile filter fabric can be used in erosion control applications, such as beneath riprap or stone layers, to prevent soil loss while allowing water to drain away.
Subgrade stabilization: It can be used as a separation and filtration layer in subgrade stabilization projects, preventing the mixing of different soil layers and promoting efficient water drainage.