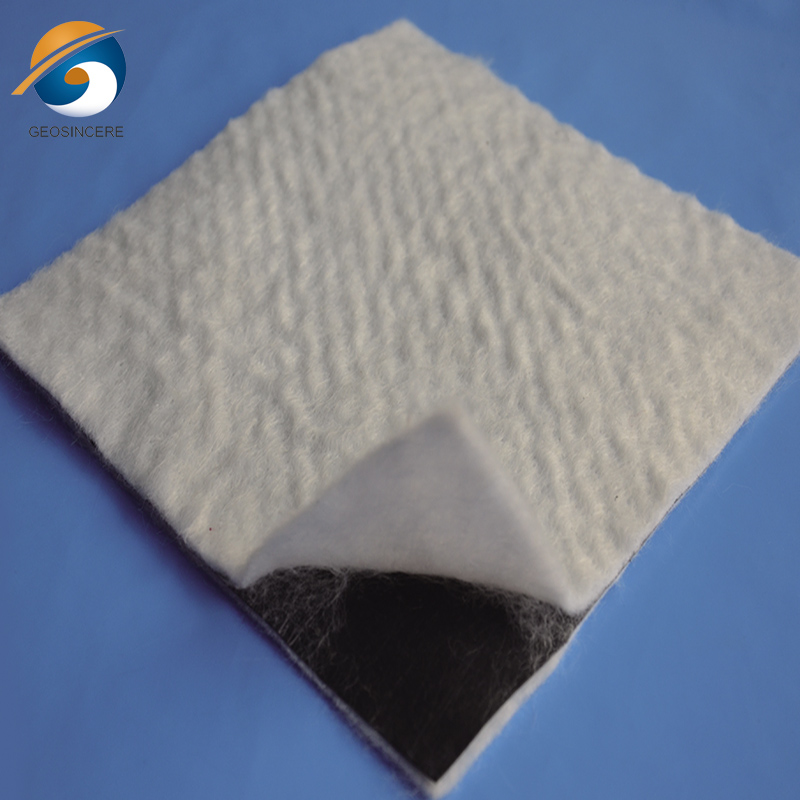
Impermeable Composite Geomembrane Plastic Dam Linings
Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings, also known as impermeable geomembranes or plastic liners, are specialized materials used to line and seal dams and reservoirs. They provide a waterproof barrier that prevents water seepage, ensuring effective water containment.They ensure the integrity and efficiency of water storage by providing a durable and impermeable barrier.
The primary function of impermeable geomembranes is to create a watertight barrier within the dam or reservoir structure. They prevent water from seeping through the dam walls or base, reducing the risk of leakage and ensuring efficient water storage.Impermeable composite geomembranes are often made with multiple layers for enhanced performance. These layers can include a core layer of impermeable plastic material sandwiched between two protective layers. The protective layers provide resistance against punctures, UV degradation, and other potential damage.
Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings are specialized liner systems designed for water containment in dam construction and rehabilitation projects.The primary purpose of impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings is to provide a barrier that prevents water seepage through the dam structure. They act as impermeable barriers to ensure effective water containment and prevent loss or leakage of water.
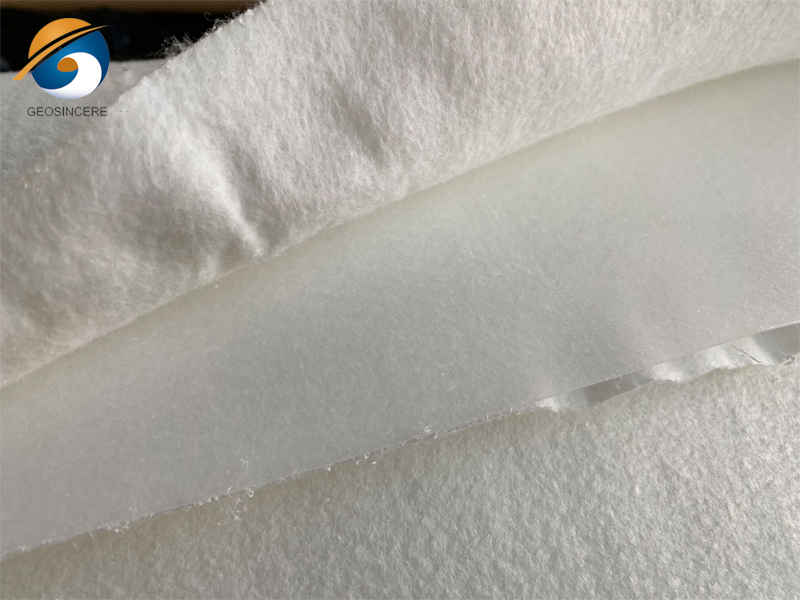
These liners are typically made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other plastic materials known for their impermeability, durability, and resistance to UV radiation, chemicals, and punctures. The liners may consist of multiple layers or a composite structure, combining different materials for enhanced performance.Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings often comprise multiple layers, each serving a specific function. For example, a typical composite structure may include a smooth HDPE layer for impermeability, a geosynthetic clay liner (GCL) for added hydraulic conductivity reduction, and a protective non-woven geotextile layer for mechanical protection.
Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings play a crucial role in preventing water leakage through the dam structure. They help maintain the desired water levels in the reservoir, prevent seepage into the surrounding soil or groundwater, and minimize the risk of dam failure.These liners are designed to withstand the challenging environmental conditions associated with dam construction. They are engineered to have excellent durability, resistance to chemical degradation, and long-term performance to ensure the integrity of the dam structure over its lifespan.
The impermeable liners contribute to environmental protection by preventing water loss, protecting downstream ecosystems, and avoiding potential soil erosion or contamination associated with uncontrolled water seepage.Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings provide a reliable solution for water containment in dam construction and rehabilitation projects. They ensure the integrity and stability of dams, reduce water loss, and contribute to the sustainable management of water resources.
Parameter
Test ltem | Test Properties | Unit | BCM4 | BCM5 | BCM5 | BCM7 | BCM8 |
Weight | g/㎡ | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | |
Film Thickness | Mm | 0.25-0.35 | 0.30-0.50 | ||||
Mechanical Properties | Break Strength | kN/m | 5.0 | 7.5 | 10.0 | 12.0 | 14.0 |
Break Elongation | % | 30-100 | 30-100 | 30-100 | 30-100 | 30-100 | |
CBR Burst Strength | KN | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 2.5 | |
Tear Resistance | KN | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.40 | 0.48 | |
Peel Strength | N/cm | ≥6 | ≥6 | ≥6 | ≥6 | ≥6 | |
Hydrostatic Pressure | Film Thickness | Mm | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 |
One cloth one film | Mpa | 0.4 | 0.5. | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 | |
Two cloth one film | Mpa | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 | |
Impermeable Composite Geomembrane Plastic Dam Linings Features
•High friction coefficient, excellent wear resistance
•Stable low temperature embrittlement resistance.
•Excellent impermeable, leak and moisture proof
•High tensile strength and tearing strength
•Excellent chemical resistance
•Anti-aging and anti-corrosion.
•High strength, anti puncture
•Easy to deploy efficiently
•Excellent UV resistance
•Cost saving
Applications of Impermeable Composite Geomembrane Plastic Dam Linings
Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings find a range of applications in various dam construction and rehabilitation projects. Here are some common applications:
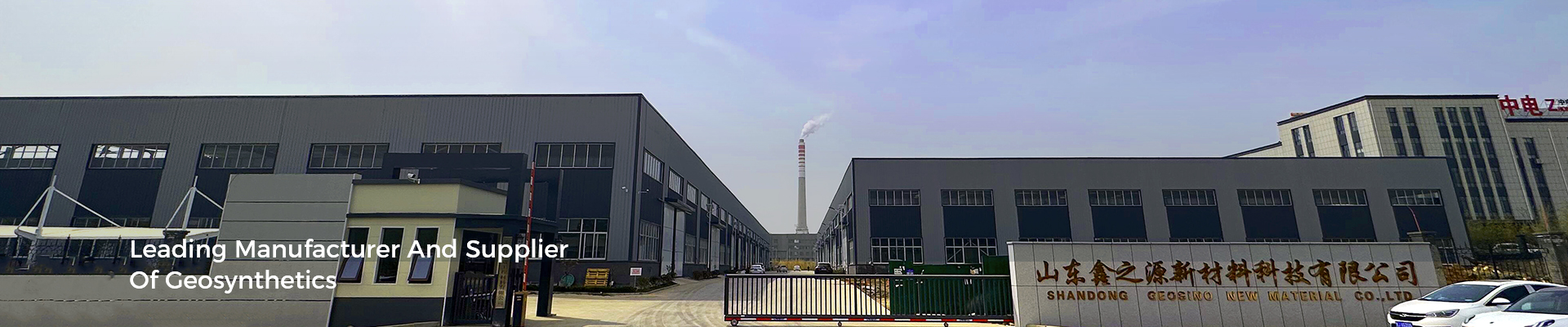
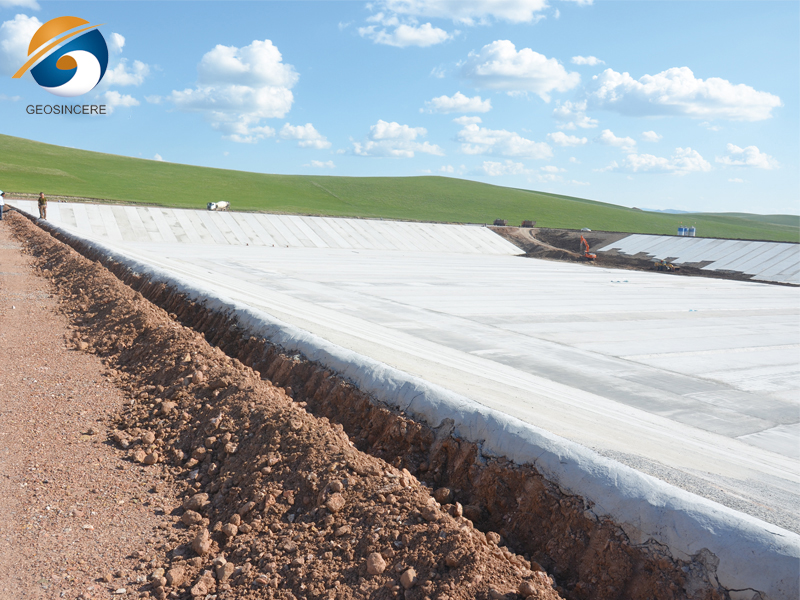
New Dam Construction: These liners are used in the construction of new dams to provide an impermeable barrier that prevents water seepage through the dam structure. They are installed on the upstream face of the dam to ensure effective water containment and prevent loss or leakage of water.
Dam Rehabilitation: Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings are also employed in the rehabilitation and repair of existing dams. They can be used to repair leaks or reinforce the existing lining system, enhancing the overall impermeability of the dam and extending its service life.
Reservoirs and Storage Ponds: These liners are utilized in the construction of reservoirs and storage ponds to create an impermeable barrier that prevents water seepage. They help maintain the desired water levels, prevent water loss, and ensure efficient water storage for various purposes, such as irrigation, drinking water supply, or industrial use.
Tailings and Waste Containment: Impermeable liners are employed in the construction of containment areas for tailings or waste materials. They create an impermeable barrier that prevents the seepage of potentially harmful substances into the surrounding environment, protecting soil and groundwater from contamination.
Irrigation Canals and Channels: Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic liners are used in irrigation systems to line canals, channels, and other water conveyance structures. They prevent water seepage, ensuring efficient water delivery to agricultural fields and reducing the loss of water resources.
Pond and Lagoon Liners: These liners are utilized in the construction of ponds and lagoons for various purposes, such as wastewater treatment, aquaculture, or stormwater management. They provide an impermeable barrier that prevents the seepage of water into the surrounding soil, ensuring effective containment and management of liquids.
Landfill Liners: Impermeable liners are employed in the construction of landfill cells or containment areas. They prevent the seepage of leachate, which is the liquid generated from waste decomposition, into the surrounding environment. This helps protect groundwater quality and minimize the risk of environmental contamination.
Mining and Industrial Applications: Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic linings are used in mining operations and industrial facilities for containment of process liquids, tailings, or other waste materials. They provide an impermeable barrier that helps prevent environmental contamination and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings are versatile and offer effective water containment solutions in a wide range of applications. They contribute to the efficient management of water resources, environmental protection, and the sustainable operation of infrastructure projects.
Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings are vital components in modern hydraulic engineering, ensuring long-term water containment, minimizing seepage, and safeguarding ecological balance. These synthetic barriers—typically composed of geotextiles and polymer-based geomembranes—are widely applied in earth dams, reservoirs, tailings ponds, and irrigation canals. This article provides an in-depth technical review of composite geomembrane dam liners, covering materials, performance characteristics, design considerations, regulatory standards, and best practices for installation and maintenance.
What is an Impermeable Composite Geomembrane?
An impermeable composite geomembrane is a laminated barrier system combining one or more layers of geotextile (nonwoven or woven) with a polymer geomembrane such as HDPE (high-density polyethylene), LLDPE (linear low-density polyethylene), or PVC (polyvinyl chloride). This configuration enhances mechanical strength, puncture resistance, chemical compatibility, and overall impermeability.
Common Structures:
One geotextile + One geomembrane (1-layer composite)
Two geotextiles + One geomembrane (2-layer composite)
Reinforced composite with central membrane and protective faces
Key Benefits of Composite Geomembrane Plastic Linings
✅ Excellent Impermeability – Water vapor transmission rate as low as <1×10⁻¹³ g·cm/(cm²·s·Pa)
✅ Chemical Resistance – Withstands exposure to acids, alkalis, and hydrocarbons
✅ High Puncture Strength – Enhanced durability under soil, rock, or hydrostatic loads
✅ UV Stability – Resists degradation under prolonged sun exposure (UV > 80% retention over 10 years)
✅ Flexibility & Weldability – Adaptable to irregular terrains and weldable for seamless coverage
Material Specifications
| Component | Description | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Geomembrane Layer | HDPE, LLDPE, PVC, EVA | ASTM D5199, D6693 |
| Geotextile Layer | PP or PET, needle-punched or woven | ASTM D5261, ISO 10319 |
| Thickness | 0.5 mm – 3.0 mm (geomembrane), 150 – 800 g/m² (geotextile) | GB/T 17643-2011 |
| Color Options | Black, white, blue (for solar reflection or leak detection) | N/A |
Applications in Dam and Reservoir Projects
Earth Dam Linings
Prevents seepage into foundation and abutments
Reduces uplift pressure and internal erosion risks
Irrigation Canals and Channels
Increases water use efficiency by reducing infiltration losses
Tailings and Wastewater Containment
Offers safe containment for leachate, heavy metals, and toxic residues
Stormwater and Rainwater Harvesting Systems
Ensures impermeability of artificial catchments
Engineering Design Considerations
1. Seepage Control and Hydraulic Head
Geomembrane design must account for maximum water depth, gradient, and subgrade permeability.
Safety factor ≥ 1.5 is recommended for critical structures.
2. Slope Stability
Composite liners must resist sliding on slopes; coefficient of friction between liner and subgrade ≥ 0.4.
Geotextile improves frictional resistance.
3. Anchor Trench Design
Liners must be securely embedded in anchor trenches at crest and toe to prevent pullout due to uplift or wave action.
4. Temperature and UV Resistance
For tropical or high-altitude sites, use UV-stabilized HDPE geomembranes rated for -40°C to +85°C.
Industry Standards and Codes
ASTM D5883 – Standard guide for geomembrane seam evaluation
ASTM D6392 – Air channel and vacuum box testing for welds
GB/T 17643-2011 (China) – Technical standard for composite geomembranes
ISO 10319 / 13426 – Mechanical and hydraulic testing of geotextiles
GSI-GM13 – HDPE geomembrane specification by Geosynthetic Institute
🔍 Ensure that both base materials and final seams meet site-specific hydraulic and structural design loads.
Installation Guidelines
Subgrade Preparation
Smooth, compacted, debris-free surface
Slope gradients ≤ 1:2 recommended
Panel Deployment
Laid from top to bottom; minimal tension to prevent stretching
Overlap minimum: 100 mm
Seaming
Hot wedge or extrusion welding for HDPE
Double-track welding with air pressure test for critical zones
Testing and QA/QC
Destructive seam testing every 150 m
Air channel pressure test (ASTM D5820)
Spark testing for electrical leaks
Case Study: Composite Geomembrane in Earth Dam Project
Location: Northern India
Material Used: 1.5mm HDPE + 300g/m² PP geotextile
Area Covered: 80,000 m²
Outcome: Reduced seepage by > 95%, 15-year design life with zero liner failure incidents after 7 years
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How long does a composite geomembrane last?
A: With proper UV stabilization and installation, service life can exceed 25–30 years, depending on exposure conditions and mechanical loading.
Q2: Can geomembranes be installed during winter?
A: Yes, but ambient temperatures below 0°C may affect weldability. Special heating protocols are needed during cold weather installations.
Q3: What is the difference between HDPE and LLDPE liners?
A: HDPE offers higher chemical resistance and rigidity, while LLDPE provides better flexibility and elongation—ideal for irregular subgrades.
Q4: Are these liners safe for potable water use?
A: Only FDA- or NSF-certified HDPE/LLDPE geomembranes should be used for drinking water applications.
Actionable Conclusion
Impermeable composite geomembrane plastic dam linings are indispensable for modern hydraulic containment systems. Their high impermeability, mechanical robustness, and adaptability to diverse terrain make them the material of choice for dams, canals, and reservoirs worldwide.
When selecting a geomembrane liner, consider:
Application environment (chemical, UV, load)
Regulatory and project-specific standards
Installation quality and inspection protocols